c CCLRC
Section 2.2
7. Harmonic cosine: (-hcs)
8. Cosine: (-cos)
In DL POLY 3 angular restraints are handled by the routine angles forces.
2.2.5
Dihedral Angle Potentials
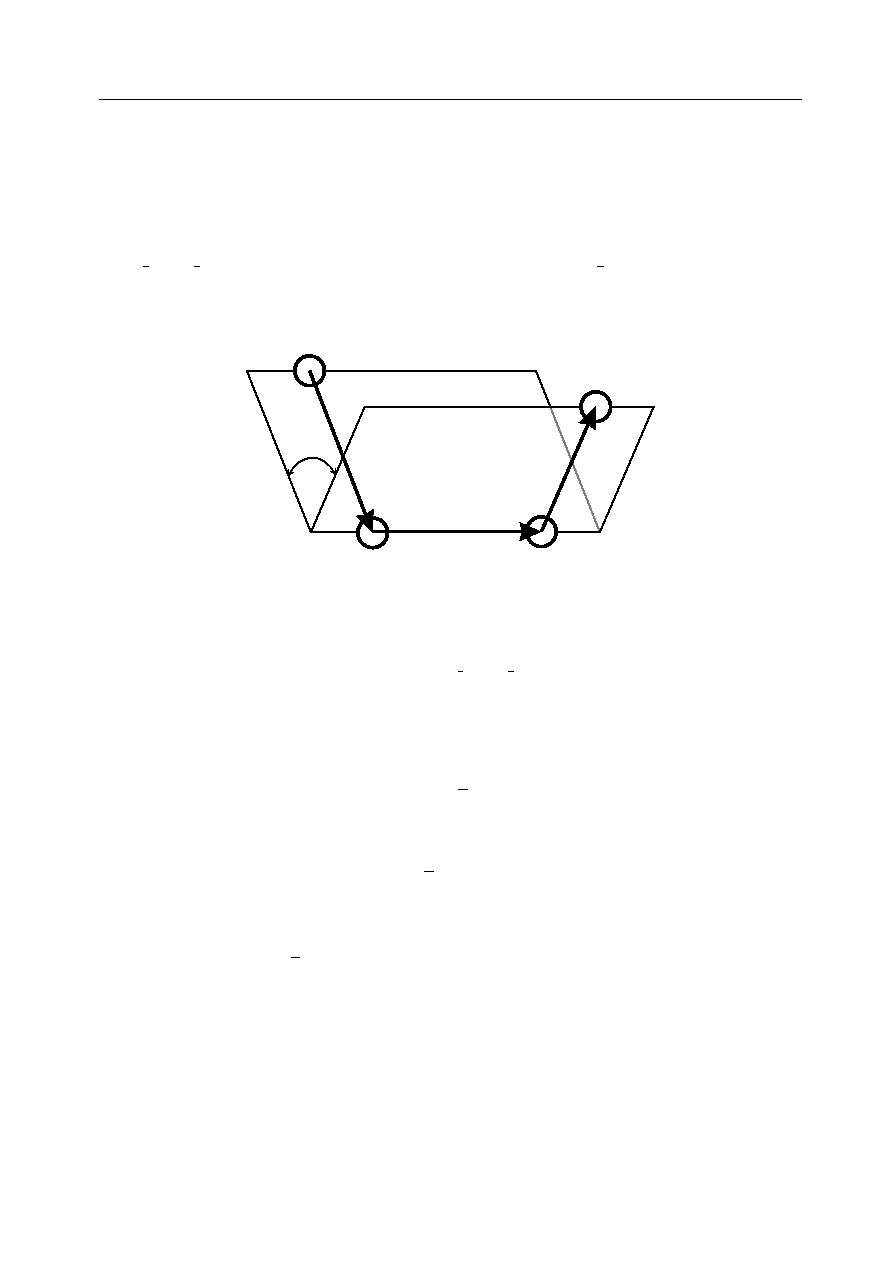
i
r
jk
r
ij
r
kn
j
k
n
The dihedral angle and associated vectors
The dihedral angle potentials describe the interaction arising from torsional forces in molecules.
(They are sometimes referred to as torsion potentials.) They require the specification of four atomic
positions. The potential functions available in DL POLY 3 are as follows:
1. Cosine potential: (cos)
U (
ijkn
) = A [1 + cos(m
ijkn
- )]
(2.31)
2. Harmonic: (harm)
U (
ijkn
) =
k
2
(
ijkn
-
0
)
2
(2.32)
3. Harmonic cosine: (hcos)
U (
ijkn
) =
k
2
(cos(
ijkn
) - cos(
0
))
2
(2.33)
4. Triple cosine: (cos3)
U () =
1
2
{A
1
(1 + cos()) + A
2
(1 - cos(2)) + A
3
(1 + cos(3))}
(2.34)
] with fixed constants a-f: (ryck)
U () = A { a + b cos() + c cos
2
() + d cos
3
() + e cos
4
() + f cos
5
() }
(2.35)
6. Fluorinated Ryckaert-Bellemans [
] with fixed constants a-h: (rbf)
U () = A { a + b cos() + c cos
2
() + d cos
3
() + e cos
4
() + f cos
5
() +
g exp(-h( - )
2
)) }
(2.36)
18

