
Gaussian 03 Online Manual
Last update: 19 September 2003
The combination of method and basis set specifies a model chemistry to Gaussian, specifying the level of theory. Every Gaussian job must specify both a method and basis set. This is usually accomplished via two separate keywords within the route section of the input file, although a few method keywords imply a choice of basis set.
The following table lists methods which are available in Gaussian, along with the job types for which each one may be used. Note that the table lists only analytic optimizations, frequencies, and polarizability calculations; numerical calculations are often available for unchecked methods (see the discussion of the specific keyword in question for details).
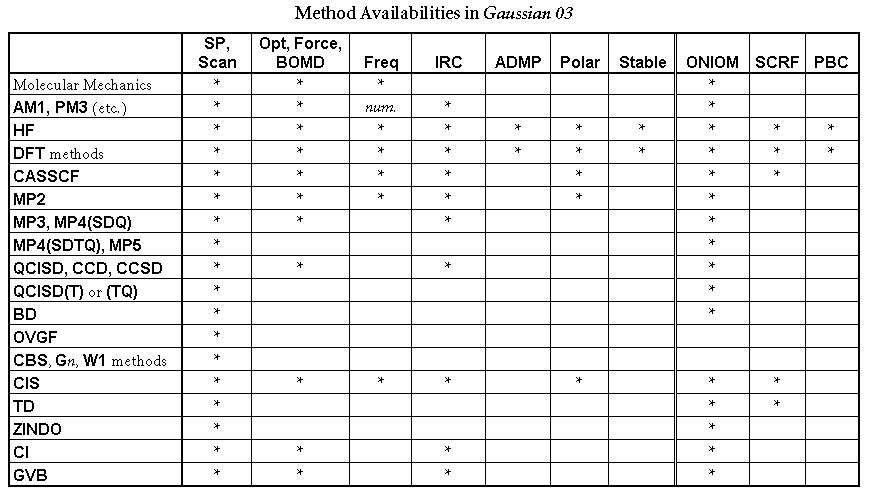
If no method keyword is specified, HF is assumed. Most method keywords may be prefaced by R for closed-shell restricted wavefunctions, U for unrestricted open-shell wavefunctions, or RO for restricted open-shell wavefunctions: for example, ROHF, UMP2, or RQCISD. RO is available only for Hartree-Fock, all Density Functional methods, AM1, MINDO3 and MNDO and PM3 semi-empirical energies and gradients, and MP2 energies; note that analytic ROMP2 gradients are not yet available.
In general, only a single method keyword should be specified, and including more than one of them will produce bizarre results. However, there are exceptions:
CASSCF may be specified along with MP2 to request a CASSCF calculation including electron correlation.
ONIOM and IRCMax jobs require multiple method specifications. However, they are given as options to the corresponding keyword.
The form model2 // model1 described previously may be used to generate an automatic optimization followed by a single point calculation at the optimized geometry.
Click here to go on to the next section.