![]()
This is another unusual MD cell (see figure), but which possesses similar advantages to the truncated octahedron, but with a slightly greater efficiency in its use of the cell volume (the ratio is about 74% to 68%).
The principal axis in the X-direction of the rhombic dodecahedron passes through the
centre of the cell and the centre of a rhombic face. The Y-axis does likewise, but is set
at 90 degrees to the X-axis. The Z-axis completes the orthonormal set and passes through a
vertex where four faces meet. If the width D of the cell is defined as the perpendicular
distance between two opposite faces, the cell vectors required for the DL_POLY_2 CONFIG
file are: (D,0,0), (0,D,0), (0,0,![]() D).These also define the enscribing orthorhombic cell,
which has twice the MD cell volume. In DL_POLY_2 the centre of the cell is also the origin
of the atomic coordinates.
D).These also define the enscribing orthorhombic cell,
which has twice the MD cell volume. In DL_POLY_2 the centre of the cell is also the origin
of the atomic coordinates.
The rhombic dodecahedron can be used with the Ewald summation method.
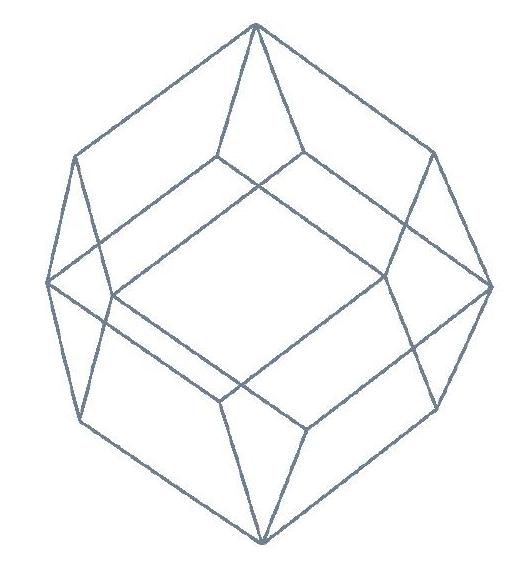
The rhombic dodecahedral MD cell.
![]()