![]()
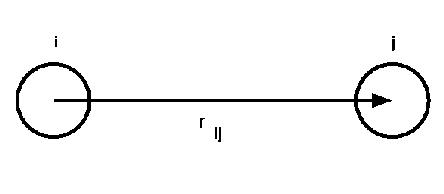
The interatomic bond vector.
The bond potentials describe explicit bonds between specified atoms. They are functions of the interatomic distance only. The potential functions available are as follows.
| (2.2) |
| (2.3) |
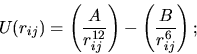 |
(2.4) |
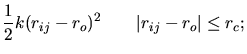 |
(2.5) | ||
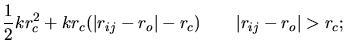 |
(2.6) |
| (2.7) |
In these formulae ![]() is the distance between atoms labelled
is the distance between atoms labelled ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
| (2.8) |
where ![]() is the position vector of an atom labelled
is the position vector of an atom labelled ![]() . 2.1
. 2.1
The force on the atom ![]() arising from a bond potential is obtained
using the general formula:
arising from a bond potential is obtained
using the general formula:
![\begin{displaymath}
\mbox{$\underline{f}$}_{j}=-\frac{1}{{r}_{ij}}\left[
\frac{\...
...}{\partial r_{ij}}U(r_{ij})\right]\mbox{$\underline{r}$}_{ij},
\end{displaymath}](img90.png) |
(2.9) |
The force ![]() acting on atom
acting on atom ![]() is the negative of this.
is the negative of this.
The contribution to be added to the atomic virial is given by
| (2.10) |
with only one such contribution from each bond.
The contribution to be added to the atomic stress tensor is given by
| (2.11) |
where ![]() and
and ![]() indicate the
indicate the ![]() components. The atomic stress tensor derived in this way is
symmetric.
components. The atomic stress tensor derived in this way is
symmetric.
In DL_POLY_2 bond forces are handled by the routine BNDFRC.
![]()