c CCLRC
Section 5.1
variable 2
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 3
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 4
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 5
real
potential parameter, see Table
The variables pertaining to each potential are described in Table
Note that any pair potential not specified in the FIELD file, will be assumed to be zero.
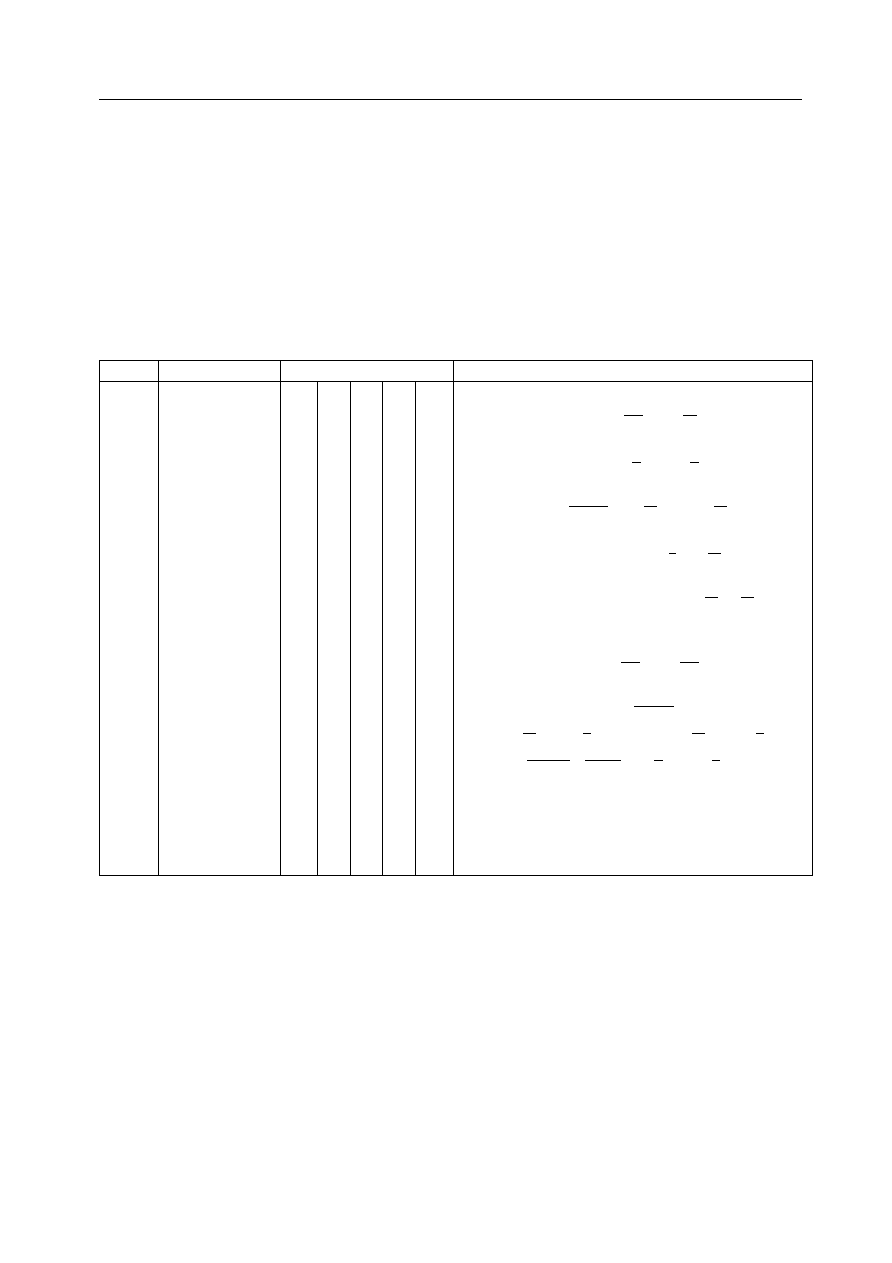
Table 5.12: Pair Potentials
key
potential type
Variables (1-5)
functional form
12-6
12-6
A
B
U (r) =
A
r
12
-
B
r
6
lj
Lennard-Jones
U (r) = 4
r
12
-
r
6
nm
n-m
E
o
n
m
r
0
U (r) =
E
o
(n-m)
m
r
o
r
n
- n
r
o
r
m
buck
Buckingham
A
C
U (r) = A exp -
r
-
C
r
6
bhm
Born-Huggins
A
B
C
D
U (r) = A exp[B( - r)] -
C
r
6
-
D
r
8
-Meyer
hbnd
12-10 H-bond
A
B
U (r) =
A
r
12
-
B
r
10
snm
Shifted force
E
o
n
m
r
0
r
c
U (r) =
E
o
(n-m)
×
m
n
r
o
r
n
-
1
n
- n
m
r
o
r
m
-
1
m
+
nmE
o
(n-m)
r-r
o
r
o
n
-
m
mors
Morse
E
0
r
0
k
U (r) = E
0
[{1 - exp(-k(r - r
0
))}
2
- 1]
tab
Tabulation
tabulated potential
Note: in this formula the terms , and are compound expressions involving the variables
E
o
, n, m, r
0
and r
c
. See Section
for further details.
Note: r
c
defaults to the general van der Waals cutoff (rvdw or rcut) if it is set to zero or not
specified or not specified in the FIELD file.
2. rdf n
where n is the number of RDF pairs to be entered. It is followed by n records, each specifying
a particular RDF pair in the following manner:
atmnam 1
a8
first atom type
atmnam 2
a8
second atom type
96

