c CCLRC
Section 5.1
variable 2
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 3
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 4
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 5
real
cutoff range for this potential (°
A)
The variables pertaining to each potential are described in Table
Note that the fifth variable is the range at which the three body potential is truncated. The
distance is in °
A, measured from the central atom.
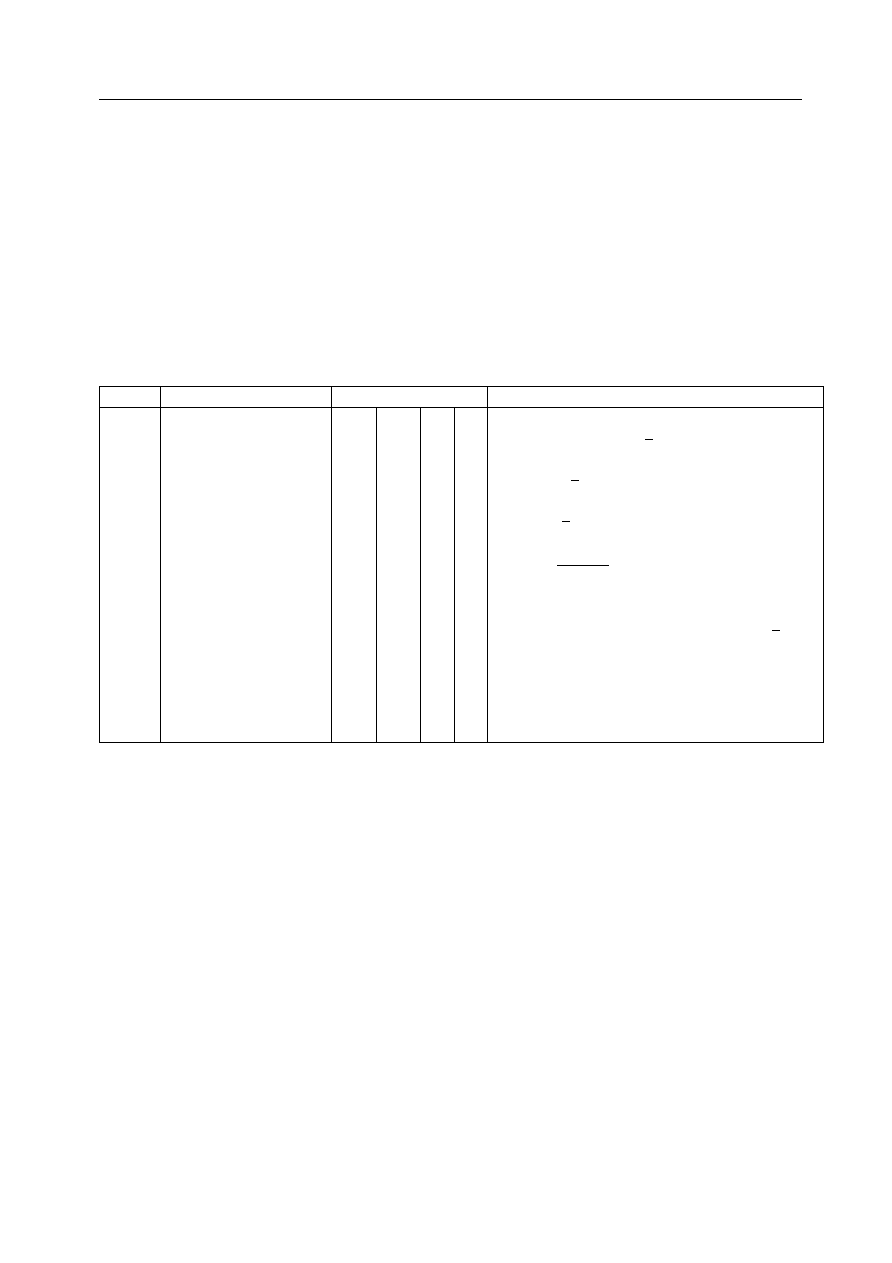
Table 5.15: Three-body Potentials
key
potential type
Variables (1-4)
functional form
harm
Harmonic
k
0
U () =
k
2
( -
0
)
2
thrm
Truncated harmonic
k
0
U () =
k
2
( -
0
)
2
exp[-(r
8
ij
+ r
8
ik
)/
8
]
shrm
Screened harmonic
k
0
1
2
U () =
k
2
( -
0
)
2
exp[-(r
ij
/
1
+ r
ik
/
2
)]
bvs1
k
0
1
2
U () =
k
8(-
0
)
2
(
0
- )
2
- ( - )
2 2
×
exp[-(r
ij
/
1
+ r
ik
/
2
)]
bvs2
k
0
a
U () = k [
a
( -
0
)
2
( +
0
- 2)
2
-
a
2
a-1
( -
0
)
2
( -
0
)
3
] exp[-(r
8
ij
+ r
8
ik
)/
8
]
hbnd
D
hb
R
hb
U () = D
hb
cos
4
()×
[5(R
hb
/r
jk
)
12
- 6(R
hb
/r
jk
)
10
]
is the i-j-k angle
6. fbp n
where n is the number of four-body potentials to be entered. It is followed by n records, each
specifying a particular metal potential in the following manner:
atmnam 1 (i)
a8
first (central) atom type
atmnam 2 (j)
a8
second atom type
atmnam 3 (k)
a8
third atom type
atmnam 3 (l)
a8
forth atom type
key
a4
potential key, see Table
variable 1
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 2
real
potential parameter, see Table
variable 3
real
cutoff range for this potential (°
A)
The variables pertaining to each potential are described in Table
99

