



Next: Four Body Potentials
Up: The Intermolecular Potential Functions
Previous: Metal Potentials
Contents
Index
The three-body potentials in DL_POLY_2 are mostly
valence angle forms. (They are
primarily included to permit simulation of amorphous materials
e.g. silicate glasses.) However, these have been extended to include
the Dreiding [8] hydrogen
bond. The potential forms available are as follows.
- Truncated harmonic: (thrm)
![\begin{displaymath}
U(\theta_{jik})= {k\over 2} (\theta_{jik} - \theta_0)^2
\exp[-(r_{ij}^8 + r_{ik}^8)/\rho^8];
\end{displaymath}](img100.png) |
(2.99) |
- Screened Harmonic: (shrm)
![\begin{displaymath}
U(\theta_{jik})= {k\over 2} (\theta_{jik} - \theta_0)^2
\exp[-(r_{ij}/\rho_1 + r_{ik}/\rho_2)] ;
\end{displaymath}](img101.png) |
(2.100) |
- Screened Vessal[24]: (bvs1)
- Truncated Vessal[25]: (bvs2)
- Dreiding hydrogen bond [8]: (hbnd
![\begin{displaymath}
U(\theta_{jik})=D_{hb}cos^{4}(\theta_{jik})[5(R_{hb}/r_{jk})^{12}-6(R_{hb}/r_{jk})^{10}]
\end{displaymath}](img266.png) |
(2.103) |
Note that for the hydrogen bond, the hydrogen atom must be the
central atom. Several of these functions are identical to those
appearing in the intra-molecular valenceangle descriptions
above. There are significant differences in implementation however,
arising from the fact that the three-body potentials are regarded as
inter-molecular. Firstly, the atoms involved are defined by
atom types, not specific indices. Secondly, there are no
excluded atoms arising from the three body terms. (The inclusion of
pair potentials may in fact be essential to maintain the structure of
the system.)
The three body potentials are very short
ranged, typically of order 3 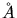 . This property, plus the fact that
three body potentials scale as
. This property, plus the fact that
three body potentials scale as 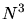 ,
where
,
where 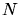 is the number of particles, makes it essential that these
terms are calculated by the link-cell method [29].
is the number of particles, makes it essential that these
terms are calculated by the link-cell method [29].
The calculation of the forces, virial and stress tensor as
described in the section valence angle potentials above.
DL_POLY_2 applies no long range corrections to the three body potentials.
The three body forces are calculated by the routine THBFRC.




Next: Four Body Potentials
Up: The Intermolecular Potential Functions
Previous: Metal Potentials
Contents
Index
W Smith
2003-05-12
![$\displaystyle {k \over 8(\theta_{jik}-\pi)^2}\left\{ \left[
(\theta_0 -\pi)^2 -(\theta_{jik}-\pi)^2\right]^2
\right\}$](img103.png)
![$\displaystyle {k \over 8(\theta_{jik}-\pi)^2}\left\{ \left[
(\theta_0 -\pi)^2 -(\theta_{jik}-\pi)^2\right]^2
\right\}$](img103.png)
![]() . This property, plus the fact that
three body potentials scale as
. This property, plus the fact that
three body potentials scale as ![]() ,
where
,
where ![]() is the number of particles, makes it essential that these
terms are calculated by the link-cell method [29].
is the number of particles, makes it essential that these
terms are calculated by the link-cell method [29].